Architecture
High Level Architecture
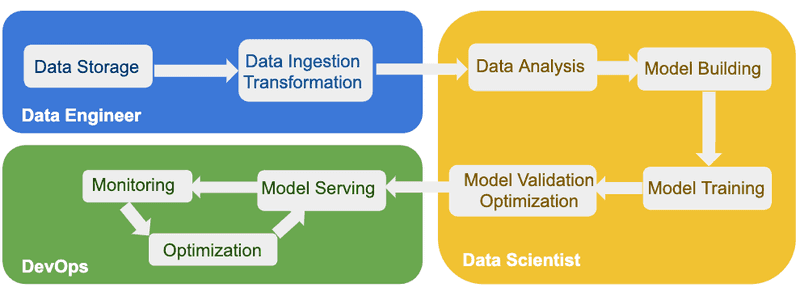
A complete end-to-end AI platform requires services for each step of the AI workflow. In general, an AI workflow includes most of the steps shown in Figure 1 and is used by multiple AI engineering personas such as Data Engineers, Data Scientists and DevOps.
The first phase of an AI workflow is initiated by Data Engineers that acquire the data from different sources and perform the required transformations. Data Engineers are also responsible to store and provide access to the transformed data to Data Scientist or Data Analysts that work on the second phase in the AI workflow. In the second phase, Data Scientists perform analysis on the transformed data and create the appropriate ML models. Once the models are trained and validated accordingly, they are ready to be served on the production platform in the last phase of the AI end-to-end workflow. In the production phase, ML models are served as services on the cluster and DevOps engineers are tasked with constantly monitoring and optimizing the services. The process does not end at this last step, Data Scientists should monitor and keep validating models based on incoming and trained data sets.
Red Hat® OpenShift® Container Platform is the leading Kubernetes based container platform providing multiple functionalities for successfully running distributed AI workloads. Functionalities such as high availability and self-healing, scaling, security, resource management and operator framework are essential to successfully providing AI/ML services. OpenShift also supports specialized hardware such as GPUs.
Open Data Hub(ODH) currently provides services on OpenShift for AI data services such as data storage and ingestion/transformation. For data storage and availability, ODH integrates seamlessly with Object Storage provider (OpenShift Data Foundation, Minio, AWS S3, ...) that exists in the Hybrid Cloud or on-premise.
Open Data Hub also provides services for model creation, training and validation. For the Data Scientist development environment, ODH provides Jupyter Notebook images running natively distributed on OpenShift. ODH roadmap includes tools for monitoring services as discussed in the section below. These tools will include the ability for natively monitoring AI services and served models on OpenShift using Prometheus and Grafana.
Open Data Hub Platform
Open Data Hub platform is a centralized self-service solution for analytic and data science distributed workloads. It is a collection of open source tools and services natively running on OpenShift.
Components and Considerations
End-to-End Considerations
ODH project’s main goal is to provide an open source end-to-end AI platform on OpenShift Container Platform that is equipped to run large AI/ML distributed workloads. As discussed earlier an end-to-end AI platform includes all phases of AI processing starting from data ingestion all the way to production AI/ML hosting and monitoring. There are multiple user personas for this platform that work on different phases.
All the tools and components listed below are currently being used as part of Red Hat’s internal ODH platform cluster. This internal cluster is utilized by multiple internal teams of data scientists running AI/ML workloads for functions such as Anomaly Detection and Natural Language Processing. A subset of these components and tools are included in the ODH release available today and the rest are scheduled to be integrated in future releases as described in the roadmap section below. Support for each component is provided by the source entity, for example Red Hat supports Red Hat components such as OpenShift Container Platform and Ceph while open source communities support Seldon, Jupyterhub, Prometheus and so on.
Data in Motion is essential in today's enterprise backend networks where data resides in multiple locations, especially to support data stored in legacy systems. Hybrid Cloud architectures also require sharing data between different cloud systems. Tools such as Red Hat AMQ Streams, Kafka and Logstash provide robust and scalable data transfer capabilities native to the OpenShift platform. Data Engineers can use these tools to transfer required data from multiple sources.
Storage: Data Lake/Databases/In-Memory includes tools for distributed file, block and object storage at scale. We include tools for both relational databases and document-oriented databases. Big data storage requires the freedom of no schema constraints while data access requires some form of ordered schema definition. Data ingestion can be easily performed using Red Hat Data Grid into distributed object storage provided by Ceph. High performance in-memory datastore solutions such as Red Hat Data Grid which is based on Infinispan are essential for fast data access needed for analysis or model training.
Metadata Management tools basically add informational metadata to the stored data such as databases, tables, columns, partitions, schemas and location. Currently, we have investigated Hive Metastore as a solution that provides an SQL interface to access the metadata information.
Data Analysis: Big Data Processing tools are needed for running large distributed AI workloads. Apache Spark™is installed as an operator on OCP providing cluster wide custom resource to launch distributed AI workloads on distributed spark clusters. These spark clusters are not shared among users, they are specific to each user providing isolation of resource usage and management. Spark clusters are also ephemeral and are deleted once the user shuts down the notebook providing efficient resource management.
Data Analysis: Data Exploration tools provide the query and visualization functions for data scientists to perform initial exploration of the data. Hue provides an SQL interface to query the data and basic visualization. Kibana is also a data visualization tool for Elasticsearch indexed data.
Data Analysis: Streaming tools such as Kafka and Elasticsearch allow for distributed and scalable message distribution native to OpenShift.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Model Lifecycle tools provide functionalities to serve the model and collect essential metrics needed to monitor the lifecycle of the model. It allows constant evaluation of model performance which can lead to the need for retraining or re-validation. Seldon is a tool that provides model hosting and metric collection from both the model itself and the component serving the model. MLflow provides parameter tracking for models and deployment functionalities.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Interactive Notebooks provide a development workspace for data scientists and business analysts to conduct their analysis work. JupyterHub is a tool that provides a multi-user notebook environment that allows users to use notebooks running in their own workspace. This allows for resource management isolation. Hue is also a multiuser data analysis platform that allows querying and plotting of data.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Business Intelligence tools such as Apache Superset provide a rich set of data visualization tools and come enterprise-ready with authentication, multi-user and security integrated.
Security and Governance include tools for providing services, data and API security and governance. Data in storage and in motion require security for both access and encryption. The Ceph Object Gateway provides encryption of uploaded objects and options for the management of encryption keys. The Ceph Object Gateway stores that data in the Ceph Storage Cluster in encrypted form. Red Hat Single Sign-On (Keycloak) and OpenShift provide user authentication while Red Hat 3Scale provides an API gateway for REST Interfaces.
Monitoring and Orchestration provide tools for monitoring all aspects of the end-to-end AI platform. This includes but is not limited to data, messaging, API, resources availability and utilization, etc. Prometheus and Grafana offer an interface for collecting and displaying metrics. For orchestration tools we included Jenkins and Argo Workflows that provide the functionality to create and manage workflows for build and release automation. Argo is OpenShift native workflow tools that can run pods in a directed acyclic graph (DAG) workflow.
Current Included Components
The ODH platform is installed on OpenShift as a native operator and is available on the OperatorHub.io. The operator framework (https://operatorhub.io/getting-started) is an open source toolkit that provides effective, scalable and automated native application management. Operators manage custom resources that provide specific cluster wide functionalities. The ODH operator manages the ODH platform AI/ML services cluster-wide. Some of the components within the ODH platform are also operators such as Apache Spark™. Currently ,when installing the ODH operator it includes the following components: Ceph, Apache Spark, Jupyterhub, Prometheus and Grafana.
Jupyter Notebook w/ JupyterLab UI (https://jupyter.org/hub) is an open source notebook platform that ODH provides with multiple notebook image streams that incorporate embedded AI/ML libraries. Jupyter Notebooks also provide many features such as for data scientists allowing them to run notebooks in their own workspaces in a multi-tenant environment. Authentication can also be customized as a pluggable component to support authentication protocols such as OAuth. Data scientists can use familiar tools such as Jupyter notebooks for developing complex algorithms and models. Frameworks such as Tensorflow, PyTorch and more are available for use.
Prometheus (https://prometheus.io/) is an open source monitoring and alerting tool that is widely adopted across many enterprises. Prometheus can be configured to monitor targets by scraping or pulling metrics from the target’s HTTP endpoint and storing the metric name and a set of key-value pairs in a time series database. For graphing or querying this data, Prometheus provides a web portal with rudimentary options to list and graph the data. It also provides an endpoint for more powerful visualization tools such as Grafana to query the data and create graphs. An Alert Manager is also available to create alert rules to produce alerts on specific metric conditions.
Grafana (https://grafana.com/) is an open source tool for data visualization and monitoring. Data sources such as Prometheus can be added to Grafana for metrics collection. Users create Dashboards that include comprehensive graphs or plots of specific metrics. It includes powerful visualization capabilities for graphs, tables, and heatmaps. Ready-made dashboards for different data types and sources are also available giving Grafana users a head start. It also has support for a wide variety of plugins so that users can incorporate community-powered visualisation tools for things such as scatter plots or pie charts.
Seldon (https://www.seldon.io) is an open source framework that makes it easier to deploy AI/ML models on Kubernetes and OpenShift. The model can be created and trained using many tools such as Apache Spark, scikit-learn and TensorFlow. Seldon also provides metric for Prometheus scraping. Metrics can be custom model metrics or Seldon core system metrics.